Neutron Diagram

Dendrites receive messages from other neurons.
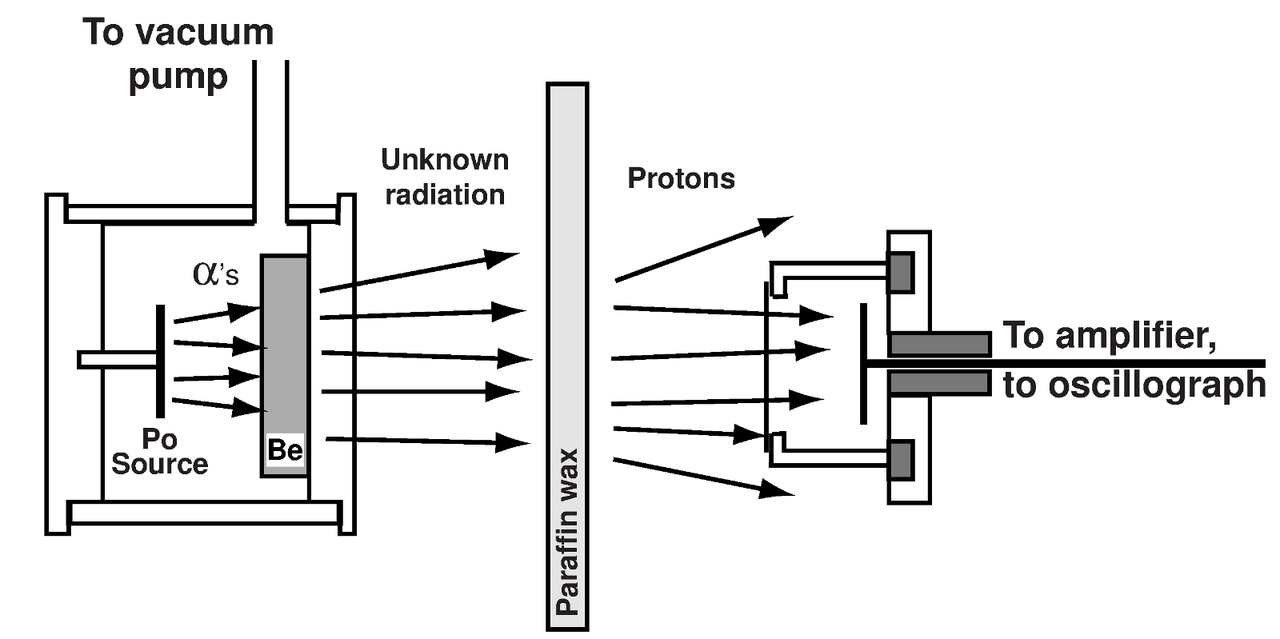
Neutron diagram. The decay of the neutron involves the weak interaction as indicated in the feynman diagram to the right. It is also known as the axon terminal the bouton the axon foot or the synaptic knob and it has the role of converting the electro chemical signal into a chemical message which travels further to the next neuron. From there the message can move to the next neuron. Choose from 500 different sets of neuron diagram flashcards on quizlet.
A free neutron will decay with a half life of about 103 minutes but it is stable if combined into a nucleus. Introduction to neurons and glia. The axon ending is as the name and the cell diagram suggest the very end of each axon. The message then moves through the axon to the other end of the neuron then to the tips of the axon and then into the space between neurons.
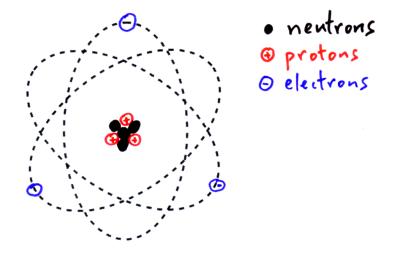
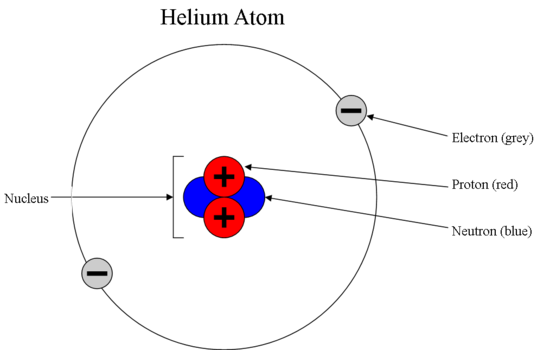
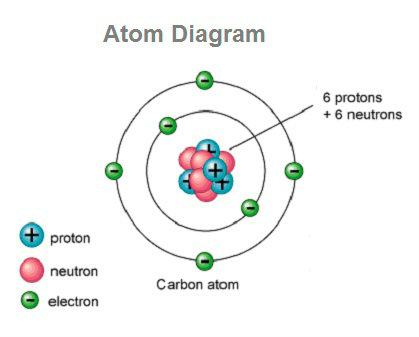
That makes the atom very stable. Overview of neuron structure and function. Alex bolano on may 29 2019leave a comment. Captionthe image on the left is a basic atom diagramthis one shows the protons neutrons and electrons of a carbon atom.
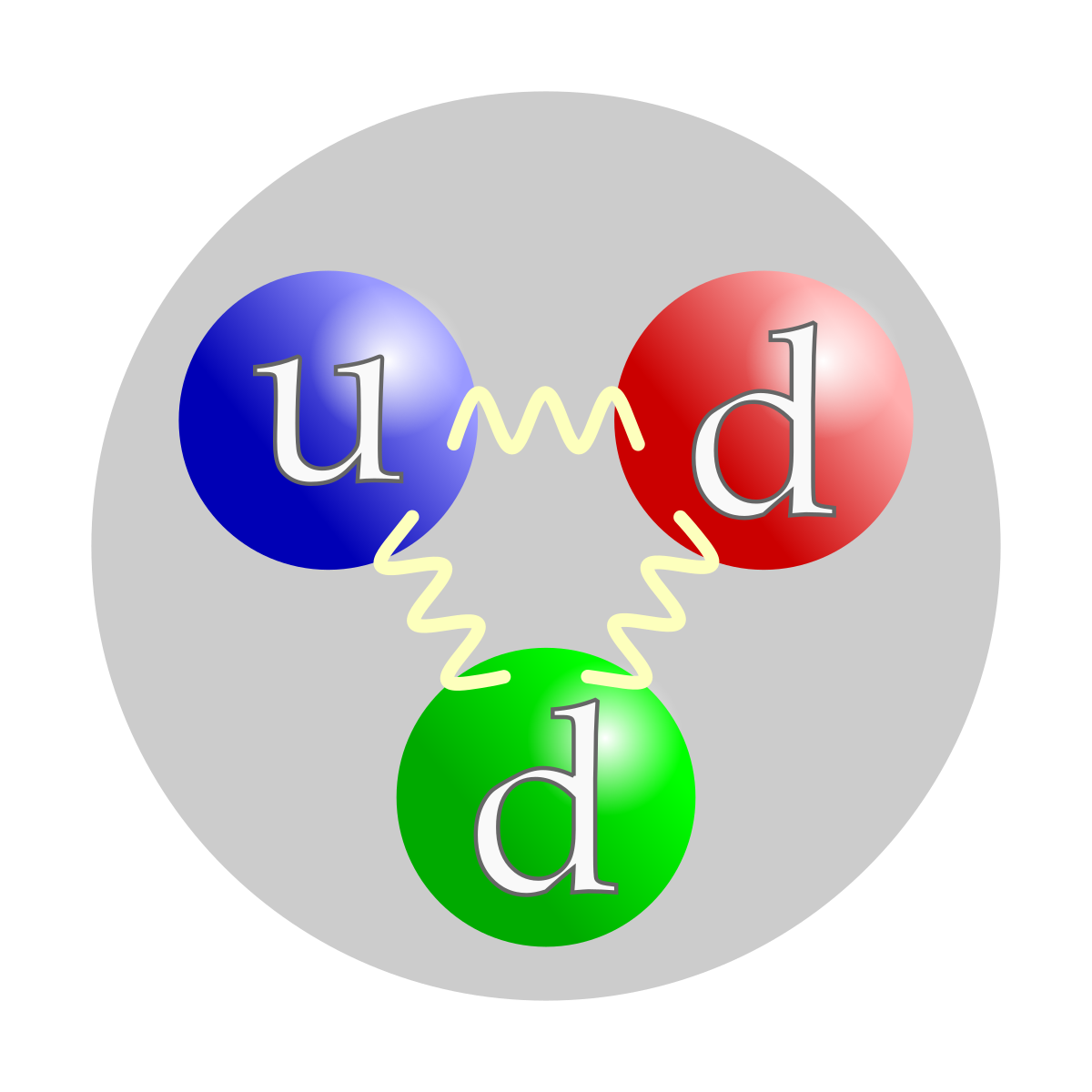
This is the currently selected item. Neurons pass messages to each other using a special type of electrical signal. The neutron is a baryon and is considered to be composed of two down quarks and one up quark. Their properties and interactions are described by.
Each is in a group of six. Anatomy of a neuron. How the structure of a neuron allows it to receive and transmit information. Neurons are the basic organizational units of the brain and nervous system.
The neuron and nervous system. A neuron also known as a neurone old british spelling or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapsesit is the main component of nervous tissueall animals except sponges and placozoans have neurons but other multicellular organisms such as plants do not. Neurons are typically classified into three types. The neutron is a subatomic particle symbol n or n 0 with no net electric charge and a mass slightly greater than that of a protonprotons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atomssince protons and neutrons behave similarly within the nucleus and each has a mass of approximately one atomic mass unit they are both referred to as nucleons.